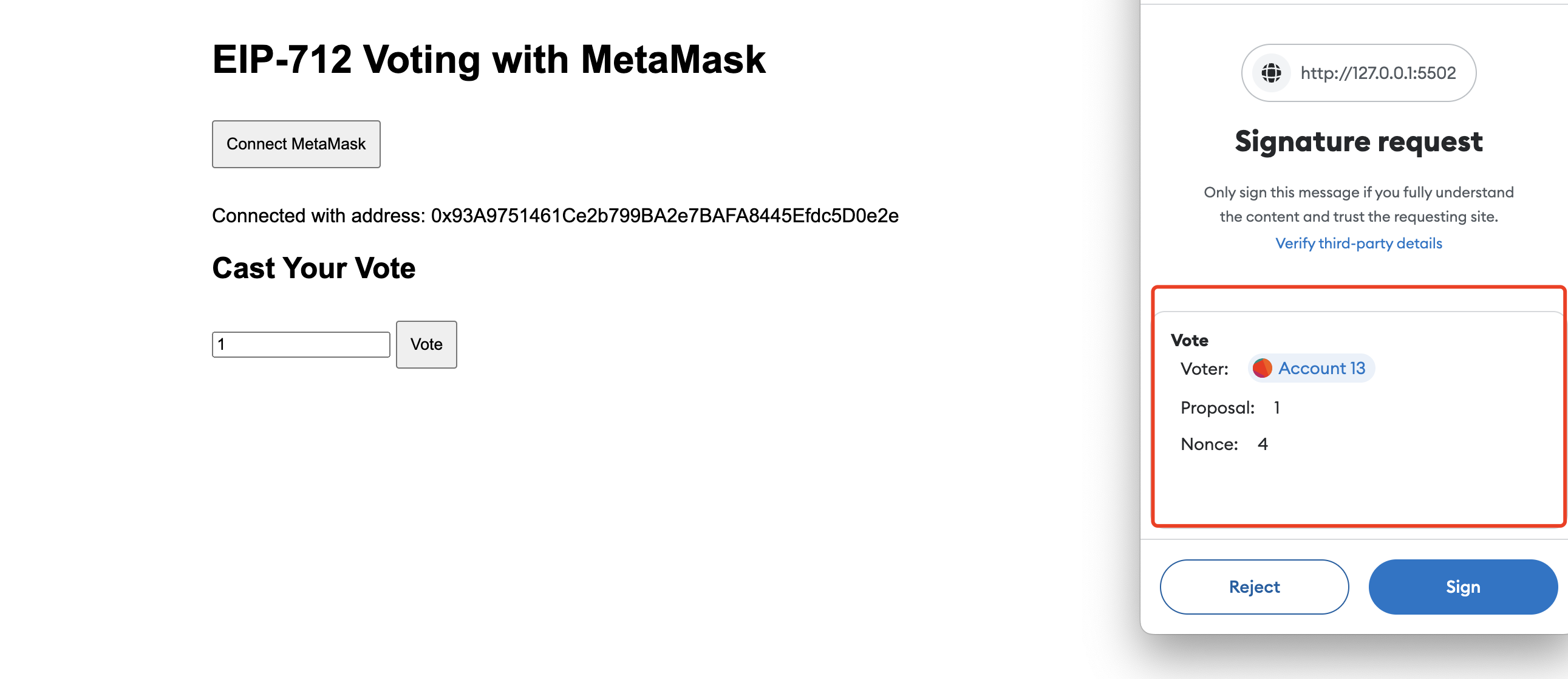
How to use EIP-712 Signature
Introduction to EIP-712
EIP-712, or "Typed structured data hashing and signing," is a standard in Ethereum Improvement Proposals. It provides a standardized way to sign structured data, making the signing process more secure and user-friendly.
Key Components of EIP-712 Signatures
-
EIP712Domain: Every EIP-712 signature must include an EIP712Domain section. This section contains crucial information about the contract and the environment:
EIP712Domain: [
{ name: "name", type: "string" },
{ name: "version", type: "string" },
{ name: "chainId", type: "uint256" },
{ name: "verifyingContract", type: "address" },
];This information is displayed during the signing process and ensures that the signature can only be verified by a specific contract on a specific chain.
-
Domain Object: In your signing script, you need to provide the domain information:
const domain = {
name: "EIP712Voting",
version: "1",
chainId: 71, // Conflux eSpace testnet
verifyingContract: "0xDD1184EeC78eD419d948887B8793E64a62f13895",
}; -
Custom Types: You need to define custom types that match your contract's structure:
const types = {
Vote: [
{ name: "voter", type: "address" },
{ name: "proposal", type: "uint256" },
{ name: "nonce", type: "uint256" },
],
}; -
Message: Create a message object with the data to be signed:
const value = {
voter: await signer.getAddress(),
proposal: 1, // Voting for proposal 1
nonce: await contract.nonces(signer.address),
}; -
Signing Process: Use the wallet's
signTypedData()method to create the signature:const signature = await signer.signTypedData(domain, types, value);
Benefits of EIP-712
- Improved Readability: Users can clearly see what they're signing, reducing the risk of malicious transactions.
- Enhanced Security: The structured format helps prevent certain types of phishing attacks.
- Better User Experience: Wallets and dApps can display more meaningful signing requests.
- Cross-Platform Consistency: Ensures consistent behavior across different Ethereum-compatible platforms.
In this tutorial, we'll implement EIP-712 signatures on the Conflux eSpace network using Hardhat, creating a simple voting system to demonstrate its usage. Our voting system will allow users to sign their votes off-chain and submit them to the blockchain, ensuring both privacy and efficiency.
1. Project Setup
First, ensure you have Node.js and npm installed. Then, create a new project directory and initialize it:
mkdir eip712-conflux-demo
cd eip712-conflux-demo
npm init -y
Install the necessary dependencies:
npm install --save-dev hardhat @nomicfoundation/hardhat-toolbox @openzeppelin/contracts dotenv
2. Configure Hardhat
Create a Hardhat configuration file hardhat.config.js:
require("@nomicfoundation/hardhat-toolbox");
require("dotenv").config();
module.exports = {
solidity: "0.8.24",
networks: {
eSpaceTestnet: {
url: "https://evmtestnet.confluxrpc.com",
accounts: [process.env.PRIVATE_KEY],
},
},
};
Create a .env file to store your private key:
PRIVATE_KEY=your_private_key_here
Make sure to add .env to your .gitignore file.
3. Write the Smart Contract
Create a contracts/EIP712Voting.sol file:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/utils/cryptography/ECDSA.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/utils/cryptography/EIP712.sol";
contract EIP712Voting is EIP712 {
using ECDSA for bytes32;
mapping(uint256 => uint256) public voteCount;
// TypeHash for the Vote struct used in EIP-712 signing
bytes32 private constant VOTE_TYPEHASH =
keccak256("Vote(address voter,uint256 proposal,uint256 nonce)");
mapping(address => uint256) public nonces;
event VoteCast(address indexed voter, uint256 indexed proposal);
constructor() EIP712("EIP712Voting", "1") {}
function castVote(uint256 proposal, bytes memory signature) external {
// Generate the hash of the structured data
bytes32 structHash = keccak256(
abi.encode(
VOTE_TYPEHASH, // Type hash of the Vote struct, ensures data structure consistency
msg.sender, // Address of the voter
proposal, // ID of the proposal being voted on
nonces[msg.sender] // Current nonce of the voter, prevents replay attacks
)
);
// structHash now contains a unique identifier of the vote data
// Generate the final hash using the EIP-712 standard's _hashTypedDataV4 function
bytes32 hash = _hashTypedDataV4(structHash);
// hash is now the final hash combining the structured data hash and the domain separator
// This final hash is used to verify the EIP-712 signature
// The domain separator includes contract name, version, chain ID, and contract address,
// ensuring the signature is only valid for this specific contract and network
address signer = ECDSA.recover(hash, signature);
require(signer == msg.sender, "EIP712Voting: Invalid signature");
voteCount[proposal]++;
nonces[signer]++;
emit VoteCast(signer, proposal);
}
function getVoteCount(uint256 proposal) external view returns (uint256) {
return voteCount[proposal];
}
}
This contract implements EIP-712 signature verification and voting functionality.
4. Write the Deployment Script
Create a scripts/deploy.js file:
const hre = require("hardhat");
async function main() {
const EIP712Storage = await hre.ethers.getContractFactory("EIP712Voting");
const eip712Storage = await EIP712Storage.deploy();
// Wait for the contract to be deployed
await eip712Storage.waitForDeployment();
// Get the deployed contract address
const address = await eip712Storage.getAddress();
console.log("EIP712Storage deployed to:", address);
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exitCode = 1;
});
5. Deploy the Contract
Run the following command to deploy the contract:
npx hardhat run scripts/deploy.js --network eSpaceTestnet
Note down the output contract address.
6. Create the Signing Script
Create a scripts/sign.js file:
const hre = require("hardhat");
require("dotenv").config();
async function main() {
const [signer] = await hre.ethers.getSigners();
const contractAddress = "<YOUR_DEPLOYED_CONTRACT_ADDRESS>";
const domain = {
name: "EIP712Voting",
version: "1",
chainId: 71, // Conflux eSpace testnet
verifyingContract: contractAddress,
};
const types = {
Vote: [
{ name: "voter", type: "address" },
{ name: "proposal", type: "uint256" },
{ name: "nonce", type: "uint256" },
],
};
const EIP712Voting = await hre.ethers.getContractFactory("EIP712Voting");
const contract = EIP712Voting.attach(contractAddress);
const nonce = await contract.nonces(signer.address);
const value = {
voter: await signer.getAddress(),
proposal: 1, // Assume we're voting for proposal 1
nonce: nonce,
};
// Use the new signTypedData method
const signature = await signer.signTypedData(domain, types, value);
console.log("Signer:", await signer.getAddress());
console.log("Proposal:", value.proposal);
console.log("Nonce:", nonce.toString());
console.log("Signature:", signature);
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exitCode = 1;
});
Remember to update contractAddress with your deployed contract address.
7. Generate the Signature
Run the signing script:
npx hardhat run scripts/sign.js --network eSpaceTestnet
This will output the signature information.
8. Create the Voting Script
Create a scripts/vote.js file:
const hre = require("hardhat");
async function main() {
const contractAddress = "<YOUR_DEPLOYED_CONTRACT_ADDRESS>";
const EIP712Voting = await hre.ethers.getContractFactory("EIP712Voting");
const contract = EIP712Voting.attach(contractAddress);
const proposal = 1; // Same as the proposal number used in the signature
const signature = "<YOUR_SIGNATURE>";
const tx = await contract.castVote(proposal, signature);
await tx.wait();
console.log("Vote cast successfully");
const voteCount = await contract.getVoteCount(proposal);
console.log("Vote count for proposal", proposal, ":", voteCount.toString());
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exitCode = 1;
});
Update contractAddress and signature with your actual values.
9. Execute the Vote
Run the voting script:
npx hardhat run scripts/vote.js --network eSpaceTestnet
This will cast a vote using the generated signature.
10. Create a Frontend Interface
Create a public/sign.html file:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>EIP-712 Voting with MetaMask</title>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/ethers/6.7.0/ethers.min.js"></script>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
max-width: 800px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 20px;
}
button {
margin: 10px 0;
padding: 10px;
}
#status,
#result,
#voteInfo {
margin-top: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>EIP-712 Voting with MetaMask</h1>
<button id="connectButton">Connect MetaMask</button>
<div id="status"></div>
<div id="votingSection" style="display:none;">
<h2>Cast Your Vote</h2>
<input
type="number"
id="proposalInput"
placeholder="Enter proposal number"
/>
<button id="voteButton">Vote</button>
</div>
<div id="result"></div>
<div id="voteInfo"></div>
<script type="module">
import { ethers } from "https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/ethers/6.7.0/ethers.min.js";
const contractAddress = "YOUR_DEPLOYED_CONTRACT_ADDRESS";
const contractABI = [
"function nonces(address owner) view returns (uint256)",
"function castVote(uint256 proposal, bytes memory signature) external",
"function getVoteCount(uint256 proposal) view returns (uint256)",
"function getVoterProposal(address voter) view returns (uint256)", // Assuming this function exists in the contract
];
let provider, signer, contract;
const connectButton = document.getElementById("connectButton");
const statusDiv = document.getElementById("status");
const votingSection = document.getElementById("votingSection");
const proposalInput = document.getElementById("proposalInput");
const voteButton = document.getElementById("voteButton");
const resultDiv = document.getElementById("result");
const voteInfoDiv = document.getElementById("voteInfo");
const checkVoteButton = document.getElementById("checkVoteButton");
connectButton.addEventListener("click", async () => {
if (typeof window.ethereum !== "undefined") {
try {
await window.ethereum.request({ method: "eth_requestAccounts" });
provider = new ethers.BrowserProvider(window.ethereum);
signer = await provider.getSigner();
contract = new ethers.Contract(
contractAddress,
contractABI,
signer
);
const address = await signer.getAddress();
statusDiv.innerHTML = ``;
votingSection.style.display = "block";
checkVoteButton.style.display = "block";
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
statusDiv.innerHTML = "Failed to connect to MetaMask";
}
} else {
statusDiv.innerHTML = "Please install MetaMask";
}
});
voteButton.addEventListener("click", async () => {
const proposal = proposalInput.value;
if (!proposal) {
alert("Please enter a proposal number");
return;
}
try {
const address = await signer.getAddress();
const nonce = await contract.nonces(address);
const domain = {
name: "EIP712Voting",
version: "1",
chainId: Number((await provider.getNetwork()).chainId),
verifyingContract: contractAddress,
};
const types = {
Vote: [
{ name: "voter", type: "address" },
{ name: "proposal", type: "uint256" },
{ name: "nonce", type: "uint256" },
],
};
const value = {
voter: address,
proposal: BigInt(proposal),
nonce: nonce,
};
const signature = await signer.signTypedData(domain, types, value);
const tx = await contract.castVote(proposal, signature);
await tx.wait();
const voteCount = await contract.getVoteCount(proposal);
resultDiv.innerHTML = ``;
} catch (error) {
console.error("Voting error:", error);
let errorMessage = error.message;
if (error.data && typeof error.data.message === "string") {
const match = error.data.message.match(
/execution reverted: (.*?)(?:\.?$)/
);
if (match) {
errorMessage = match[1];
}
}
resultDiv.innerHTML = "Failed to cast vote: " + errorMessage;
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
This HTML file provides a simple user interface for connecting MetaMask, casting votes, and checking voting results.
11. Run the Frontend
Use Live Server or another HTTP server to run public/sign.html. Make sure to update contractAddress with your deployed contract address.
结论
Through this tutorial, you've learned how to implement EIP-712 signatures on Conflux eSpace using Hardhat. This includes writing and deploying smart contracts, generating and verifying signatures, and creating a simple frontend interface to interact with the contract.
Remember to always protect your private keys and thoroughly test your application on testnets before conducting any real transactions.